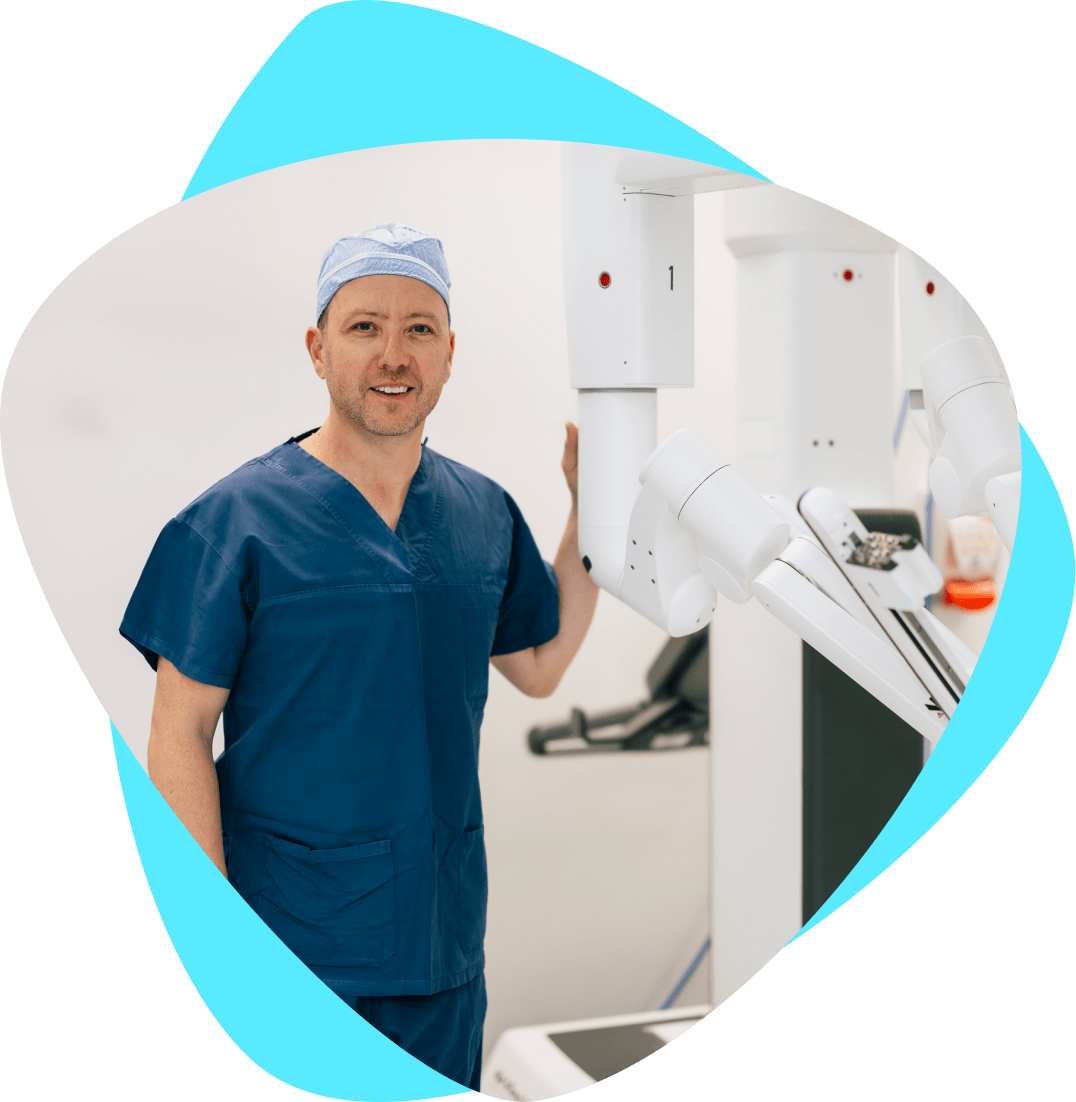
Dr Savdie is certified in robotic surgery, using the cutting-edge da Vinci robotic surgical system, as well as having trained extensively in laparoscopic surgery. He has a keen interest in urological research and holds a significant scientific publication list in the field, particularly in prostate cancer.
Dr Savdie completed a Bachelor of Science (BSc) in 1999, and then a Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, Hons) in 2003 at the University of Sydney, graduating medicine with Honours. He then undertook his urological surgical training in NSW and the ACT, and completed a Master of Surgery (MS) Degree with a focus on prostate cancer while undertaking surgical training.
Dr Savdie achieved Fellowship of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons (FRACS) in 2013, graduating as a consultant urologist. He then undertook additional sub-specialised surgical training, completing a 1-year Fellowship in minimally invasive and robotic surgery at St Vincent’s Hospital Sydney, working under luminary urologists recognised for their expertise in cancer surgery. He then embarked on a lengthy 2-year surgical training Fellowship at the internationally renowned Vancouver Prostate Centre and at the University of British Columbia, Canada to further train in his sub-specialisation.
Dr Savdie offers both a general urological care, as well as providing complex surgical services for benign and cancerous conditions. He specialises in diseases of the prostate, kidneys, bladder and testes. He offers some of the latest treatment modalities for BPH, including Rezūm and HoLEP minimally-invasive therapies.
Dr Savdie performs a range of minor surgical procedures, including vasectomy, adult circumcision and kidney stone removal, as well as performing reconstructive surgery for Peyronie’s Disease (penile curvature) and inflatable penile prosthesis for those suffering from impotence often as a result of cancer surgery or radiation therapy.
Dr Savdie welcomes both private and public patients.
During his 2-year Fellowship at the Vancouver Prostate Centre, Dr Savdie conducted novel research on new MRI diagnostic tools for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. He also helped develop urine and blood-based DNA assays for the detection of bladder cancer. Dr Savdie has more than 25 peer reviewed scientific papers and has presented his research regularly at the annual AUA meeting in the USA, the largest international meeting on Urology. He is also a regular reviewer for Journal of Urology and Urologic Oncology.
Publication list:





